✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2385
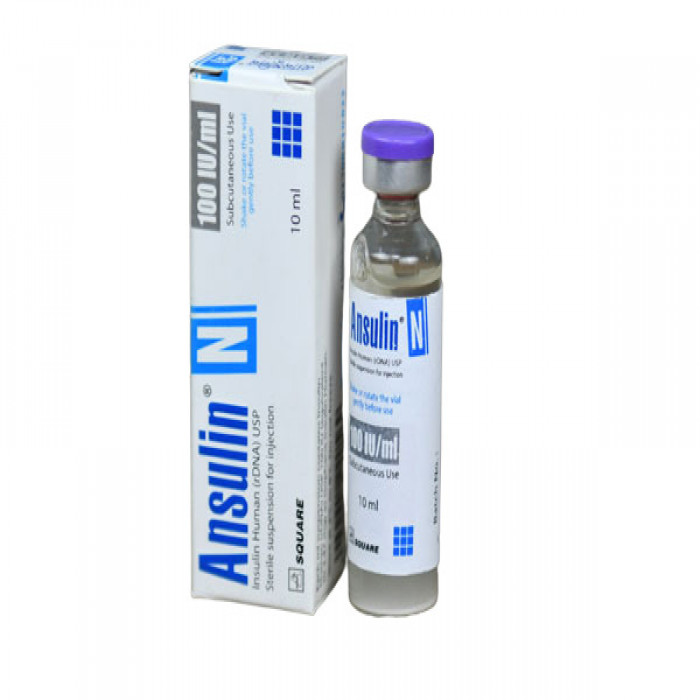
Ansulin N 100IU Vial
Human insulin is used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus (Type 1 & Type 2).
Discount
Price: ৳ 394
MRP:
৳
415
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
- Ansulin N 100IU Vial contains Biphasic Isophane Insulin.
- Therapeutic Group: Antidiabetic agents.
- Used to treat diabetes mellitus (both type I and type II).
- Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by abnormally high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
- It can occur due to inadequate production of insulin (a hormone produced by the pancreas to metabolize glucose) in the body or due to inadequate sensitivity of body cells to the actions of insulin.
- Biphasic Isophane Insulin is a pre-mixed combination of Regular (soluble) insulin and Isophane (NPH) insulin.
- It is fast-acting, starting to lower blood sugar levels within 30 minutes.
- It should be injected 30 minutes before a meal, and meals should be consumed within the next 30 minutes.
- Talk to your doctor before starting therapy with Ansulin N 100IU Vial, especially if you have liver, kidney, or heart problems.
- Inform your doctor if you have any hormonal problems.
- Notify your doctor if you have made sudden changes to your diet or perform intense exercise.
- Do not use this medicine if you have hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels).
Safety Advices

Alcohol
UNSAFE
Avoid consumption of alcohol while taking this medicine as it could aggravate your existing disease condition.

Pregnancy
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Ansulin N 100IU Vial can be used during pregnancy if prescribed by the physician. Therefore, consult your doctor before administration.

Breastfeeding
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Ansulin N 100IU Vial is considered safe for use during breastfeeding. However, consult your doctor before administration.

Driving
UNSAFE
Do not drive or operate any heavy tools or machines if your ability is affected by Ansulin N 100IU Vial.

Kidney
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Ansulin N 100IU Vial should be used with caution in patients with kidney problems. Therefore, consult your doctor before administration.

Liver
CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR
Ansulin N 100IU Vial should be used with caution in patients with liver problems. Therefore, consult your doctor before administration.
✔️ Uses of Ansulin N 100IU Vial
- Treats diabetes mellitus (both type I and type II)
✔️ How does Ansulin N 100IU Vial work?
Human insulin is a short-acting insulin, which starts working within 30 minutes after injection. It works similar to the insulin produced by the body. Insulin facilitates the reuptake of sugar in muscle and fat cells and also suppresses the production of sugar in the liver.
✔️ Side Effects of
Allergic reactions. Injection site reaction, lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash, lipoatrophy, hypokalaemia, blurred vision. Hypoglycaemia, insulin resistance
✔️ Quick Suggestions:
- Take it 20 to 30 minutes before a meal.
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar level) is a common side effect. Learn how to identify and manage its symptoms (sweating, rapid heartbeat, weakness, blurry vision, headache) and teach your family as well.
- Injection below the skin of the abdomen results in faster absorption than other injection sites.
- Injection sites must be rotated to prevent hard lumps from developing at one site.
- Opened vials/cartridges are good at room temperature for up to 4 weeks, while unopened vials must be placed in the refrigerator (2°C–8°C).
✔️ Indication
- Insulatard is used to treat all patients with type 1 diabetes.
- It is also prescribed for patients with type 2 diabetes who cannot be adequately controlled with diet and/or oral hypoglycemic agents.
- Additionally, it is used for patients with conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis, nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome, and severe infections or operations where initial diabetes stability is crucial.
- Treatment of gestational diabetes is another indication.
✔️ Pharmacology
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels. It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism by inhibiting hepatic glucose production and lipolysis, and enhancing peripheral glucose disposal. The various insulin formulations are classified according to their durations of action after SC Inj. They are divided into short-, intermediate-, or long-acting insulin. Soluble insulin (also known as 'neutral insulin' or 'regular insulin') is a short-acting preparation. To extend the duration of action of insulin, preparations are formulated as suspensions in 2 methods. The 1st method involves complexing insulin with a protein so that it is slowly released, e.g. protamine zinc insulin (contains an excess of protamine) and isophane insulin (or NPH insulin which contains equal amounts of protamine and insulin). An alternative method is particle size modification e.g. insulin zinc suspensions. While all the formulations can be admin by SC inj, most by IM inj, only soluble insulin can be admin by IV. Compared to SC inj, IM admin usually has a faster onset of action, with a shorter duration of action.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of
Adult Dose
Subcutaneous Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Suggested guidelines for beginning dose Usual daily maintenance range is 0.5-1 unit/kg/day SC in divided doses; nonobese may require 0.4-0.6 unit/kg/day; obese may require 0.8-1.2 units/kg/day Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Adult: Usual insulin requirement: 0.3-0.6 IU/kg/day; may be given in 1-2 divided doses. The dose should be individualized, to be adjusted according to the patient's needs. Suggested guidelines for beginning dose: 0.2 unit/kg/day May be used alone or in combination with a fast-acting insulin. Change insulin doses in small increments: Type 1 diabetes (2 unit change); type 2 diabetes (2-4 unit change). Look for consistent pattern in blood sugars for >3 days When combined with regular insulin: Morning Give two-thirds of daily insulin SC Ratio of regular insulin to NPH insulin 1:2 Evening Give one-third of daily insulin SC Ratio of regular insulin to NPH insulin 1:1 Dosing Considerations Dosage of human insulin, must be based on the results of blood and urine glucose tests and must be carefully individualized to optimal effect Dose adjustments should be based on regular blood glucose testing Adjust to achieve appropriate glucose control Hepatic impairment: Dosage reduction may be needed.
Child Dose
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus <12 years: Safety and efficacy not established >12 years: Suggested dose is 0.5-1 unit/kg/day SC; use adult dosing; usual daily maintenance range in adolescents is <1.2 units/kg/day during growth spurts
Renal Dose
Renal impairment: Dose adjustments may be needed.
Administration
Administer within 15 minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal. Administer subcutaneously in the upper arm, thigh, or abdominal wall. A subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall results in a faster absorption than from other injection sites. NPH Insulin suspensions are never to be administered intravenously.
✔️ Interaction
Possible absence of hypoglycaemic warning symptoms with beta-blockers. Decreased hypoglycaemic effect with corticosteroids, danazol, diazoxide, diuretics, glucagon, isoniazid, phenothiazine derivatives, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents, thyroid hormones, oestrogens, progestins (e.g. in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors and atypical antipsychotic (e.g. olanzapine and clozapine). Increased hypoglycaemic effect with oral antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, MAOIs, pentoxifylline, propoxyphene, salicylates and sulfonamide antibiotics. Decreased insulin resistance with octreotide and lanreotide. Increased risk of wt gain and peripheral oedema with pioglitazone, rosiglitazone. Decreased effect of sermorelin.
✔️ Contraindications
Hypoglycaemia. Hypersensitivity to any of the components.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
There are no restrictions on using insulin during pregnancy, as it does not pass the placental barrier.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
- Stopping treatment or inadequate dosing, especially in type 1 diabetes, can lead to high blood sugar.
- Symptoms of hyperglycemia may appear gradually and include thirst, increased urination, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and more.
- Severe hyperglycemia, if untreated, can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which can be fatal.
- Hypoglycemia can occur if meals are skipped or vigorous physical exercise is not planned.
- Patients with well-controlled blood sugar may experience changes in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycemia.
- Appropriate counseling is recommended.
- Long-term warning symptoms for diabetes patients may disappear.
✔️ Storage Conditions
- Store in a refrigerator (2°C-8°C) without freezing.
- Keep the container cartridge or vial in the outer carton to protect from light.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.